A systematic review of Alzheimer's disease: exploring genetic and environmental risk factors, biomarkers, and future pharmacotherapy for cognitive decline and neurodegeneration
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69857/joapr.v13i3.929Keywords:
Cholinergic neurodegeneration, Memory impairment, Synaptic dysfunction, Tau protein aggregation, Amyloid-beta pathology, NeuroinflammationAbstract
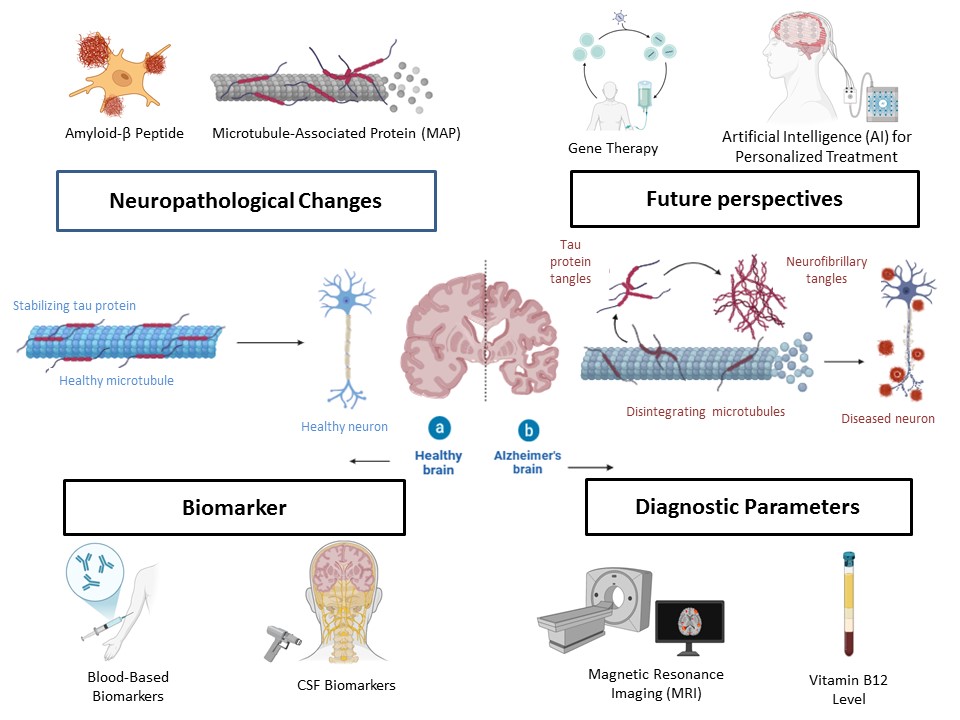
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most prevalent form of dementia, affecting millions globally through progressive cognitive decline caused by neurodegeneration in cholinergic brain regions. Aging is the primary risk factor, but metabolic, genetic, and environmental influences, including inflammation and vascular dysfunction, significantly contribute to disease onset and progression. Methodology: This comprehensive review evaluates diagnostic methods, biomarkers, and genetic and environmental risk factors associated with AD, focusing on recent advancements (2022–2025). The study selection process prioritized clinical trials, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses related to AD pathophysiology, diagnostics, and therapeutic interventions while excluding research with ambiguous findings or lacking methodological rigor. A PRISMA flowchart illustrates the study selection process, ensuring transparency. Pharmaceutical and non-pharmacological interventions, along with multi-target therapeutic strategies, were critically analyzed. Results and Discussion: AD pathology is driven by amyloid-beta plaques and tau tangles, leading to synaptic dysfunction and neurodegeneration. Current treatments, including acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists, offer symptomatic relief but are ineffective in halting disease progression. Emerging therapies such as monoclonal antibodies (Lecanemab, Donanemab), tau inhibitors, and neuroinflammation modulators show potential in slowing cognitive decline and preserving neuronal health. Advances in biomarker-based diagnostics (e.g., p-tau217) and AI-powered precision medicine have improved early detection and personalized treatment strategies, though challenges in cost, accessibility, and regulatory approval persist. Conclusion: A multisystem approach combining pharmacotherapy, biomarker-driven diagnostics, and AI-assisted personalized medicine is essential to optimize AD treatment effectiveness. Future research should focus on developing innovative, multidisciplinary treatment strategies to enhance patient outcomes and quality of life.
Downloads
References
Lane CA, Hardy J, Schott JM. Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol., 25(1), 59–70 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13439.
Tiwari S, Atluri V, Kaushik A, Yndart A, Nair M. Alzheimer’s disease: pathogenesis, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Int. J. Nanomedicine, 14, 5541–5554 (2019) https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S200490.
Savelieff MG, Nam G, Kang J, Lee HJ, Lee M, Lim MH. Development of therapeutic strategies targeting metal–amyloid interactions in Alzheimer’s disease. Coord. Chem. Rev., 351, 116–146 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2017.08.013.
Uddin MS, Mamun AA, Kabir MT, Barreto GE, Islam MS, Behl T, Perveen A, Ashraf GM. Pharmacological approaches to mitigate neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. Immunopharmacol., 84, 106479 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106479.
Kepp KP. Bioinorganic chemistry of Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Rev., 112(10), 5193–5239 (2012) https://doi.org/10.1021/cr2001393.
Ryman DC, Acosta-Baena N, Aisen PS, Bird T, Danek A, Fox NC, Goate A, Frommelt P, Ghetti B, Langbaum JB, Lopera F. Symptom onset in autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology, 83, 253–260 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000000596.
Kang J, Lemaire HG, Unterbeck A, Salbaum JM, Masters CL, Grzeschik KH, Multhaup G, Beyreuther K, Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature, 325, 733–736 (1987) https://doi.org/10.1038/325733a0.
Verghese PB, Castellano JM, Holtzman DM. Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol., 10, 241–252 (2011) https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(10)70325-2.
Allen M, Carrasquillo MM, Funk C, Heavner BD, Zou F, Younkin CS, Burgess JD, Chai HS, Crook JE, Eddy JA, Li H, Logsdon BA, Peters MA, Dang KK, Wang X, Serie DJ, Wang C, Nguyen T, Lincoln S, Malphrus K, Bisceglio G, Li Y, Kachadoorian M, Medway C, Pankratz VS, Asmann Y, Lincoln SJ, Grupe A, Reddy KL, Karypis G, Schork NJ, Price ND, Caselli RJ, Reiman EM, Younkin SG, Ertekin-Taner N. Late-onset Alzheimer disease risk variants mark brain regulatory loci. Neurol. Genet., 1, e15 (2015) https://doi.org/10.1212/NXG.0000000000000012.
Neuner SM, Tcw J, Goate AM. Genetic architecture of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis., 143, 104976 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104976.
Andrews SJ, Goate A, Anstey KJ. Association between alcohol consumption and Alzheimer’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. bioRxiv, (2017) https://doi.org/10.1101/190165.
Torres AK, Jara C, Park S, Rábano A, Hetz C, Inestrosa NC. Synaptic mitochondria: An early target of amyloid-β and tau in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis, 84, 1391–1414 (2021) https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-215139.
Bloom GS. Amyloid-β and tau: the trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol, 71, 505–508 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.5847.
Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, Charbonneau S, Whitehead V, Collin I, Cummings JL, Chertkow H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc, 53, 695–699 (2005) https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53221.x.
van Oostveen WM, de Lange ECM. Imaging techniques in Alzheimer’s disease: A review of applications in early diagnosis and longitudinal monitoring. Int J Mol Sci, 22, 2110 (2021) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22042110.
Alruwaili M, Basri R, AlRuwaili R, Albarrak AM, Ali NH. Neurological implications of vitamin B12 deficiency in diet: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Healthcare, 11, 958 (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11070958.
Arboleda-Velasquez JF, Lopera F, O’Hare M, Delgado-Tirado S, Marino C, Chmielewska N, Saez-Torres KL, Amadoru S, Schultz AP, Sperling RA, Johnson KA, Chen K, Reiman EM, Quiroz YT. Resistance to autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease in an APOE3 Christchurch homozygote: a case report. Nat Med, 25, 1680–1683 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0611-3.
Roberts JS, Patterson AK, Uhlmann WR. Genetic testing for neurodegenerative diseases: Ethical and health communication challenges. Neurobiol Dis, 141, 104871 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104871.
Snowden JS, Stopford CL, Julien CL, Gibbons L, Davies R, Thompson JC, Neary D, Mann DMA, Richardson AMT, Snowden SJ, Wear HJ, Williams-Gray CH. The clinical diagnosis of early-onset dementias: diagnostic accuracy and clinicopathological relationships. Brain, 134, 2478–2492 (2011) https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr189.
Creavin ST, Wisniewski S, Noel-Storr AH, Trevelyan CM, Hampton T, Rayment D, Thom VM, Nash KJ, Elham A, Milligan R, Patel AS, Tsivos DV, Wing T, Phillips E, Adams CE, Julious SA, Cullum SJ. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the detection of Alzheimer’s dementia and other dementias. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev., 6, CD011145 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011145.
Langa KM, Plassman BL, Wallace RB, Herzog AR, Heeringa SG, Ofstedal MB, Burke JR, Fisher GG, Fultz NH, Hurd MD, Potter GG, Rodgers WL, Steffens DC, Weir DR, Willis RJ, Welsh-Bohmer KA. The aging, demographics, and memory study: Study design and methods. Neuroepidemiology, 25, 181–191 (2005) https://doi.org/10.1159/000087448.
Antonioni A, Brandi M, Tagliabue A, Prunas O, Benussi A. Frontotemporal dementia, where do we stand? A narrative review. Int J Mol Sci, 24, 11732 (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411732.
Tripathi M, Vibha D. Reversible dementias. Indian J Psychiatry, 51(Suppl1), S52 (2009) Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3038529/.
Geldmacher DS, Whitehouse PJ. Differential diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology, 48(Suppl 6), 2S (1997) https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.48.5_suppl_6.2s.
Yanagida K, Tagami S, Okochi M. Cerebrospinal fluid and blood biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. World J Psychiatry, 1, 8 (2011) https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v1.i1.8.
Tanzi RE, Kovacs DM, Kim TW, Moir RD, Guenette SY, Wasco W. The gene defects responsible for familial Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis, 3, 159–168 (1996) https://doi.org/10.1006/nbdi.1996.0016.
Strozyk D, Blennow K, White LR, Launer LJ. CSF Aβ42 levels correlate with amyloid-neuropathology in a population-based autopsy study. Neurology, 60, 652–656 (2003) https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000046581.81650.d0.
Jack CR, Knopman DS, Jagust WJ, Shaw LM, Aisen PS, Weiner MW, Petersen RC, Trojanowski JQ. Hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers of the Alzheimer’s pathological cascade. Lancet Neurol, 9, 119–128 (2010) https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(09)70299-6.
Skoog I, Andreasson U, Lavebratt C, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Wahlund LO. Low cerebrospinal fluid Aβ42 and Aβ40 are related to white matter lesions in cognitively normal elderly. J Alzheimers Dis, 62, 1877 (2018) https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-170950.
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science, 297, 353–356 (2002) https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1072994.
Tapiola T, Alafuzoff I, Herukka SK, Parkkinen L, Hartikainen P, Soininen H, Pirttilä T. Cerebrospinal fluid β-amyloid 42 and tau proteins as biomarkers of Alzheimer-type pathologic changes in the brain. Arch Neurol, 66, 382–389 (2009) https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2008.596.
Weiner MW, Veitch DP, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Cairns NJ, Cedarbaum J, Green RC, Harvey D, Jack CR, Jagust WJ, Liu E, Morris JC, Petersen RC, Saykin AJ, Shaw LM, Toga AW, Trojanowski JQ. The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative: A review of papers published since its inception. Alzheimers Dement, 8(Suppl 1), S1–S68 (2012) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2011.09.172.
Knopman DS, Jack CR, Wiste HJ, Weigand SD, Vemuri P, Lowe VJ, Kantarci K, Gunter JL, Senjem ML, Boeve BF, Petersen RC. Selective worsening of brain injury biomarker abnormalities in cognitively normal elderly persons with β-amyloidosis. JAMA Neurol, 70, 1030–1038 (2013) https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.182.
Jack CR, Knopman DS, Jagust WJ, Shaw LM, Aisen PS, Weiner MW, Petersen RC, Trojanowski JQ. Tracking pathophysiological processes in Alzheimer’s disease: An updated hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers. Lancet Neurol, 12, 207–216 (2013) https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70291-0.
Coppens S, Lehmann S, Hopley C, Hirtz C. Neurofilament-Light, a Promising Biomarker: Analytical, Metrological and Clinical Challenges. Int J Mol Sci, 24, 11624 (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411624.
Barro C, Chitnis T, Weiner HL. Blood neurofilament light: a critical review of its application to neurologic disease. Ann Clin Transl Neurol, 7, 2508–2523 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.51234.
Zetterberg H, Skillbäck T, Mattsson N, Trojanowski JQ, Shaw LM, Blennow K. Association of cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light concentration with Alzheimer disease progression. JAMA Neurol, 73, 60–67 (2016) https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.3037.
Tarawneh R, D’Angelo G, Crimmins D, Herries E, Griest T, Fagan AM, Holtzman DM. Visinin-like protein-1: Diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in Alzheimer disease. Ann Neurol, 70, 274–285 (2011) https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22448.
Kivisäkk P, Janelidze S, Smith R, Zetterberg H, Hansson O. Increased levels of the synaptic proteins PSD-95, SNAP-25, and neurogranin in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther, 14, 58 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-022-01002-x.
McGrowder DA, Miller F, Nwokocha CR, Anderson-Jackson L, Bryan S, Asemota H, Walters C, Brown D. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease: Current evidence and future perspectives. Brain Sci, 11, 56 (2021) https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020215.
Gylys KH, Fein JA, Yang F, Wiley DJ, Miller CA, Cole GM. Synaptic changes in Alzheimer’s disease: Increased amyloid-β and gliosis in surviving terminals is accompanied by decreased PSD-95 fluorescence. Am J Pathol, 165, 1809–1817 (2004) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63436-0.
Camporesi E, Nilsson P, Brinkmalm A, Becker B, Ashton NJ, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Gobom J, Höglund K, Portelius E. Fluid biomarkers for synaptic dysfunction and loss. Biomark Insights, 15, 1177271920950319 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1177/1177271920950319.
Leuzy A, Mattsson-Carlgren N, Palmqvist S, Janelidze S, Dage JL, Hansson O. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol Med, 14, e14408 (2021) https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.202114408.
Ashton NJ, Leuzy A, Lim YM, Troakes C, Hortobágyi T, Höglund K, Aarsland D, Lovestone S, Blennow K, Zetterberg H. A multicentre validation study of the diagnostic value of plasma neurofilament light. Nat Commun, 12, 6439 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23620-z.
Albert MS, DeKosky ST, Dickson D, Dubois B, Feldman HH, Fox NC, Gamst A, Holtzman DM, Jagust WJ, Petersen RC, Snyder PJ, Carrillo MC, Thies B, Phelps CH. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement, 7, 270–279 (2011) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.008.
Ashton NJ, Janelidze S, Al Khleifat A, Leuzy A, van der Ende EL, Karikari TK, Benedet AL, Lantero-Rodriguez J, Brix B, Westwood S, Lovestone S, Zetterberg H, van der Flier WM, Teunissen CE, Rohrer JD, Blennow K. The validation status of blood biomarkers of amyloid and phospho-tau assessed with the 5-phase development framework for AD biomarkers. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 48, 2140–2156 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-021-05253-y.
Apostolova LG, Thompson PM, Green AE, Hwang KS, Zoumalan C, Jack CR Jr, Harvey DJ, Petersen RC, Thal LJ, Aisen PS, Toga AW, Cummings JL, Decarli C. Conversion of mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer disease predicted by hippocampal atrophy maps. Arch Neurol, 63, 693–699 (2006) https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.63.5.693.
De Leon MJ, Mosconi L, Blennow K, DeSanti S, Zinkowski R, Mehta PD, Pradella G, Tsui WH, Saint Louis LA, Rich K, Woolever M, Sobanska L, Brys M, Pirraglia E, Glodzik L, Switalski R, Rusinek H, Wallin A, deBernardis J, Reisberg B, Wisniewski T, Pratico D, Fowler J, de Leon M. Imaging and CSF studies in the preclinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1097, 114–145 (2007) https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1379.012.
Sternberg Z, Leurgans SE, Yu M, Datta P, Reiss AB, Eimer WA, Bennett DA, Schneider JA. Anti-Hypertensives Reduce the Rate of Alzheimer’s Disease Progression: A Cohort Study Linked with Genetic and Neuropathological Analyses. J Prev Alzheimers Dis, 11, 1634–1646 (2024) https://doi.org/10.14283/jpad.2024.156.
Jack CR Jr, Petersen RC, Xu YC, O'Brien PC, Waring SC, Tangalos EG, Smith GE, Ivnik RJ. Prediction of AD with MRI-based hippocampal volume in mild cognitive impairment. Neurology, 52, 1397–1403 (1999) https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.52.7.1397.
Haftenberger M, Lahmann PH, Panico S, Gonzalez CA, Seidell JC, Boeing H, Hallmans G, Engeset D, Skeie G, Fahey M, et al. Physical activity of subjects aged 50–64 years involved in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). Public Health Nutr., 5, 1163–77 (2002) https://doi.org/10.1079/PHN2002397.
Palmqvist S, Mattsson N, Hansson O. Accuracy of brain amyloid detection in clinical practice using cerebrospinal fluid β-Amyloid 42: A cross-validation study against amyloid positron emission tomography. JAMA Neurol., 71, 1282–89 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1001/JAMANEUROL.2014.1358.
Mattsson N, Zetterberg H, Nielsen M, Blennow K, Donohue M, Brooks DJ, Pontecorvo MJ, Friedrichsen K, Collins L, Stephens A, et al. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Detection of amyloid positivity in Alzheimer’s disease using cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers: An autopsy-confirmed study. Lancet Neurol., 14, 147–55 (2015) https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70256-9.
Nakamura A, Kaneko N, Villemagne VL, Kato T, Doecke J, Dore V, Fowler C, Martins R, Rowe C, Tomita T, et al. High performance plasma amyloid-β biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature, 554, 249–54 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25456.
Ovod V, Ramsey KN, Mawuenyega KG, Bollinger JG, Hicks T, Schneider T, Sullivan M, Lee J, Lah JJ, Levey AI, et al. Amyloid β concentrations and stable isotope labeling kinetics of human plasma specific to central nervous system amyloidosis. Alzheimers Dement., 13, 841–49 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2017.06.2266.
Schindler SE, Bollinger JG, Ovod V, Mawuenyega KG, Li Y, Gordon BA, Holtzman DM, Morris JC, Benzinger TLS, Fagan AM, et al. High-precision plasma β-amyloid 42/40 predicts current and future brain amyloidosis. Neurol., 93, e1647–59 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000008081.
Verberk IMW, van der Flier WM, Scheltens P, Teunissen CE. Plasma amyloid as prescreener for the earliest Alzheimer pathological changes. Ann. Neurol., 84, 648–58 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25367.
Janelidze S, Mattsson N, Palmqvist S, Smith R, Beach TG, Serrano GE, Chai X, Proctor NK, Eichenlaub U, Zetterberg H, et al. Plasma P-tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease: Relationship to other biomarkers, differential diagnosis, neuropathology and longitudinal progression to Alzheimer’s dementia. Nat. Med., 26, 379–86 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0755-1.
Sridhar GR. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (Galantamine, Rivastigmine, and Donepezil). NeuroPsychopharmacother., 2022, 2709–21 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62059-2_418.
Kutzing MK, Luo V, Firestein BL. Protection from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity by memantine. Ann. Biomed. Eng., 40, 1170 (2011) https://doi.org/10.1007/S10439-011-0494-Z.
Reichman HR, Farrell CL, Del Maestro RF. Effects of steroids and nonsteroid anti-inflammatory agents on vascular permeability in a rat glioma model. J. Neurosurg., 65, 233–37 (1986) https://doi.org/10.3171/JNS.1986.65.2.0233.
Di Meo F, Caruso A, Margarucci S, Petrella A, Galderisi U, Crispi S, et al. Ginkgo biloba prevents oxidative stress-induced apoptosis blocking p53 activation in neuroblastoma cells. Antioxidants, 9, 279 (2020) https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIOX9040279.
Ameen TB, Eltabl MA, Salah M, Ali A, Salem M, Mahfouz M, et al. Unraveling Alzheimer’s: the promise of aducanumab, lecanemab, and donanemab. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg., 60, 1–12 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1186/S41983-024-00845-5.
Congdon EE, Ji C, Tetlow AM, Jiang Y, Sigurdsson EM. Tau-targeting therapies for Alzheimer disease: current status and future directions. Nat. Rev. Neurol., 19, 715 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1038/S41582-023-00883-2.
Blyufer A, Liu G, Potashkin JA. Riluzole: A neuroprotective drug with potential as a novel anti-cancer agent (Review). Int. J. Oncol., 59, 95 (2021) https://doi.org/10.3892/IJO.2021.5275.
Carroll JC, Rosario ER, Villeneuve S, Burns MP, Holloway K, Pike CJ. Progesterone and estrogen regulate Alzheimer-like neuropathology in female 3xTg-AD mice. J. Neurosci., 27, 13357 (2007) https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2718-07.2007.
Dahlén AD, Da Cunha MS, da Silva CG, Ghosh A, Cheng F. Trends in antidiabetic drug discovery: FDA approved drugs, new drugs in clinical trials and global sales. Front. Pharmacol., 12, 807548 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3389/FPHAR.2021.807548.
Marucci G, Buccioni M, Dal Ben D, Lambertucci C, Volpini R. Efficacy of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology, 190, 108352 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NEUROPHARM.2020.108352.
Grossberg GT. Cholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: getting on and staying on. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp., 64, 216 (2003) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-393X(03)00059-6.
Barrachina M, Maes T, Buesa C, Ferrer I. Lysosome-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP-1) in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol., 32, 505–16 (2006) https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1365-2990.2006.00756.X.
Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Bienias JL, Evans DA, Wilson RS. Neuropathology of older persons without cognitive impairment from two community-based studies. Neurol., 66, 1837–44 (2006) https://doi.org/10.1212/01.WNL.0000219668.47116.E6.
Aarsland D, Ballard CG, Halliday G. Are Parkinson’s disease with dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies the same entity? J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol., 17, 137–45 (2004) https://doi.org/10.1177/0891988704267470.
Arnold SE, Hyman BT, Flory J, Damasio AR, Van Hoesen GW. The topographical and neuroanatomical distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Cereb. Cortex, 1, 103–16 (1991) https://doi.org/10.1093/CERCOR/1.1.103.
Aisen PS, Vellas B, Hampel H. Moving towards early clinical trials for amyloid-targeted therapy in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., 12, 324 (2013) https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3842-c1.
Hampel H, Toschi N, Babiloni C, Baldacci F, Black KL, Bokde ALW, et al. The Amyloid-β Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry, 26, 5481 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01249-0.
Burns A, Byrne EJ, Maurer K. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet, 360, 163–165 (2002) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09420-5.
Masters CL, Simms G, Weinman NA, Multhaup G, McDonald BL, Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 82, 4245–4249 (1985) https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245.
Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, Hampel H, Molinuevo JL, Blennow K, Dekosky ST, Gauthier S, Selkoe D, Bateman R, Cappa S, Crutch S, Engelborghs S, Frisoni GB, Fox NC, Galvin JE, Habert MO, Jessen F, Jicha GA, La Joie R. Advancing research diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer’s disease: The IWG-2 criteria. Lancet Neurol., 13, 614–629 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70090-0.
Hardy JA, Higgins GA. Alzheimer’s disease: The amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science, 256, 184–185 (1992) https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1566067.
Thal DR, Rüb U, Orantes M, Braak H. Phases of Aβ-deposition in the human brain and its relevance for the development of AD. Neurology, 58, 1791–1800 (2002) https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.58.12.1791.
Zheng H, Koo EH. Biology and pathophysiology of the amyloid precursor protein. Mol. Neurodegener., 6, 27 (2011) https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-6-27.
Rosen DR, Martin-Morris L, Luo L, White K. A Drosophila gene encoding a protein resembling the human β-amyloid protein precursor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 86, 2478–2482 (1989) https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.86.7.2478.
Braak H, Alafuzoff I, Arzberger T, Kretzschmar H, Tredici K. Staging of Alzheimer disease-associated neurofibrillary pathology using paraffin sections and immunocytochemistry. Acta Neuropathol., 112, 389–404 (2006) https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0127-z.
Braak H, Del Tredici K. From the Entorhinal Region via the Prosubiculum to the Dentate Fascia: Alzheimer Disease-Related Neurofibrillary Changes in the Temporal Allocortex. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 79, 163–172 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/nlz123.
Arriagada PV, Growdon JH, Hedley-Whyte ET, Hyman BT. Neurofibrillary tangles but not senile plaques parallel duration and severity of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology, 42, 631–639 (1992) https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.42.3.631.
Llamas-Rodríguez J, Martínez-González C, Villalba-Moreno NV, Ayala-Ruiz C, Torres-Sánchez I, Cañete T, Sánchez-Puebla L, Roldán-Valadez E. Entorhinal Subfield Vulnerability to Neurofibrillary Tangles in Aging and the Preclinical Stage of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis., 87, 1379–1394 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-215567.
Trejo-Lopez JA, Yachnis AT, Prokop S. Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics, 19, 173–187 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1007/S13311-021-01146-Y.
Glenner GG, Wong CW. Alzheimer’s disease: Initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 120, 885–890 (1984) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-291X(84)80190-4.
Kosik KS, Joachim CL, Selkoe DJ. Microtubule-associated protein tau (τ) is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 83, 4044–4048 (1986) https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.83.11.4044.
Wood JG, Mirra SS, Pollock NJ, Binder LI. Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer disease share antigenic determinants with the axonal microtubule-associated protein tau (τ). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 83, 4040–4043 (1986) https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.83.11.4040.
Ayers JI, Giasson BI, Borchelt DR. Prion-like Spreading in Tauopathies. Biol. Psychiatry, 83, 337–346 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOPSYCH.2017.04.003.
Aoyagi A, Condello C, Stöehr J, Yue W, Rivera BM, Lee JC, Woerman AL, Halliday G, van Duinen S, Becker AG, Prusiner SB. Aβ and tau prion-like activities decline with longevity in Alzheimer’s disease brains. Sci. Transl. Med., 11, eaat8462 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1126/SCITRANSMED.AAT8462.
Condello C, Stöehr J. Aβ propagation and strains: Implications for the phenotypic diversity in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis., 109, 191–200 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NBD.2017.03.014.
Lemere CA, Masliah E. Can Alzheimer disease be prevented by amyloid-beta immunotherapy? Nat. Rev. Neurol., 6, 108–119 (2010) https://doi.org/10.1038/NRNEUROL.2009.219.
Zhang Y, Chen H, Li R, Sterling K, Song W. Amyloid β-based therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: challenges, successes and future. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther., 8, 1–26 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1038/S41392-023-01484-7.
Nasb M, Tao W, Chen N. Alzheimer’s disease puzzle: delving into pathogenesis hypotheses. Aging Dis., 15, 43–73 (2024) https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2023.0608
Sun BL, Chen Y, Fan DY, Zhu C, Zeng F, Wang YJ. Critical thinking on amyloid-beta-targeted therapy: challenges and perspectives. Sci. China Life Sci., 64, 926–937 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1810-y
Liu X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Chen W, Zhao T, Li Z, Zhou Y, Zhang L, He Y. Clusterin transduces Alzheimer-risk signals to amyloidogenesis. Signal Transduct. Target Ther., 7, 325 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01157-x
Ailshire JA, Clarke P. Fine particulate matter air pollution and cognitive function among U.S. older adults. J. Gerontol. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci., 70, 322–328 (2015) https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/gbu064
Costa LG, Cole TB, Dao K, Chang YC, Coburn J, Garrick JM. Effects of air pollution on the nervous system and its possible role in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. Pharmacol. Ther., 210, 107523 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107523
Allen JL, Liu X, Weston D, Prince L, Oberdörster G, Finkelstein JN, Johnston CJ, Cory-Slechta DA. Developmental neurotoxicity of inhaled ambient ultrafine particle air pollution: parallels with neuropathological and behavioral features of autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders. Neurotoxicology, 59, 140–154 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2015.12.014
Andersson J, Oudin A, Sundström A, Forsberg B, Adolfsson R, Nordin M. Road traffic noise, air pollution, and risk of dementia – results from the Betula project. Environ. Res., 166, 334–339 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.06.008
Kawahara M, Kato-Negishi M. Link between aluminum and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: the integration of the aluminum and amyloid cascade hypotheses. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis., 2011, 276393 (2011) https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/276393
Huat TJ, Camats-Perna J, Newcombe EA, Valmas N, Kitazawa M, Medeiros R. Metal toxicity links to Alzheimer’s disease and neuroinflammation. J. Mol. Biol., 431, 1843–1868 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2019.01.018
Aschner M, Aschner JL. Mercury neurotoxicity: mechanisms of blood-brain barrier transport. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 14, 169–176 (1990) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0149-7634(05)80217-9
Aranda-Rivera AK, Cruz-Gregorio A, Arancibia-Hernández YL, Hernández-Cruz EY, Pedraza-Chaverri J. RONS and oxidative stress: an overview of basic concepts. Oxyg., 2, 437–478 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen2040030
Krishnamurthy HK, Madhu LN, Kabekkodu SP, Nayak PG. Oxidative stress: fundamentals and advances in quantification techniques. Front. Chem., 12, 1470458 (2024) https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2024.1470458
Gao C, Jiang J, Tan Y, Chen S. Microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target Ther., 8, 1–37 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-023-01588-0
Kraft AD, Harry GJ. Features of microglia and neuroinflammation relevant to environmental exposure and neurotoxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 8, 2980–3018 (2011) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8072980
Chen GF, Xu TH, Yan Y, Zhou YR, Jiang Y, Melcher K, Xu HE. Amyloid beta: structure, biology and structure-based therapeutic development. Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 38, 1205–1235 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.28
Jia Q, Deng Y, Qing H. Potential therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease targeting or beyond beta-amyloid: insights from clinical trials. Biomed. Res. Int., 2014, 837157 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/837157
Elmore S. Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol., 35, 495–516 (2007) https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701320337
Balali-Mood M, Naseri K, Tahergorabi Z, Khazdair MR, Sadeghi M. Toxic mechanisms of five heavy metals: mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, and arsenic. Front. Pharmacol., 12, 643972 (2021) https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.643972
Kandimalla R, Vallamkondu J, Corgiat EB, Gill KD. Understanding aspects of aluminum exposure in Alzheimer’s disease development. Brain Pathol., 26, 139–147 (2015) https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12333
Alleva E, Rankin J, Santucci D. Neurobehavioral alteration in rodents following developmental exposure to aluminum. Toxicol. Ind. Health, 14, 209–221 (1998) https://doi.org/10.1177/074823379801400113
Onyeaka H, Egbuna C, Mosa A, Adewale OB, Ifemeje JC, Nwodo UU. Preventing chemical contaminants in food: challenges and prospects for safe and sustainable food production. Food Control, 155, 110040 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2023.110040
Jaishankar M, Tseten T, Anbalagan N, Mathew BB, Beeregowda KN. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol., 7, 60–72 (2014) https://doi.org/10.2478/intox-2014-0009
Congdon EE, Sigurdsson EM. Tau-targeting therapies for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol., 14, 399–415 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-018-0013-z
Heneka MT, Carson MJ, El Khoury J, Landreth GE, Brosseron F, Feinstein DL, Jacobs AH, Wyss-Coray T, Vitorica J, Ransohoff RM, Herrup K, Frautschy SA, Finsen B, Brown GC, Verkhratsky A, Yamanaka K, Koistinaho J, Latz E, Halle A, Petzold GC, Town T, Morgan D, Shinohara ML, Perry VH, Holmes C, Bazan NG, Brooks DJ, Hunot S, Joseph B, Deigendesch N, Garaschuk O, Boddeke E, Dinarello CA, Breitner JC, Cole GM, Golenbock DT, Kummer MP. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol., 14, 388–405 (2015) https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(15)70016-5
Bhardwaj S, Singh S, Singh AP, Dwivedi UN, Singh PK. CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing: new hope for Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics. J. Adv. Res., 40, 207–221 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2021.07.001
Liu XY, Yang LP, Zhao L. Stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. World J. Stem Cells, 12, 787–802 (2020) https://doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i8.787
Appelbaum LG, Shenasa MA, Stolz L, Daskalakis ZJ. Synaptic plasticity and mental health: methods, challenges and opportunities. Neuropsychopharmacology, 48, 113–131 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-022-01370-w
Schork NJ. Artificial intelligence and personalized medicine. Cancer Treat. Res., 178, 265–283 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16391-4_11
Pais M, Pupi A, Sorbi S, Caraci F. Early diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: new definitions and challenges. Braz. J. Psychiatry, 42, 431–441 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-4446-2019-0735
Wills OC, Probst YC. Understanding lifestyle self-management regimens that improve the life quality of people living with multiple sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Qual. Life Outcomes, 20, 153 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-022-02046-1
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Debraj Dey, Deepannita Roy Mukherjee, Abu Shoeb, Pinki Biswas, Saikat Santra

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
















