Phytochemical analysis, antioxidant potential, and cytotoxic activity of extracts of Quisqualis indica L.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69857/joapr.v13i3.1215Keywords:
Quisqualis indica, flavonoids, DPPH, MTT, antioxidant, cytotoxicityAbstract
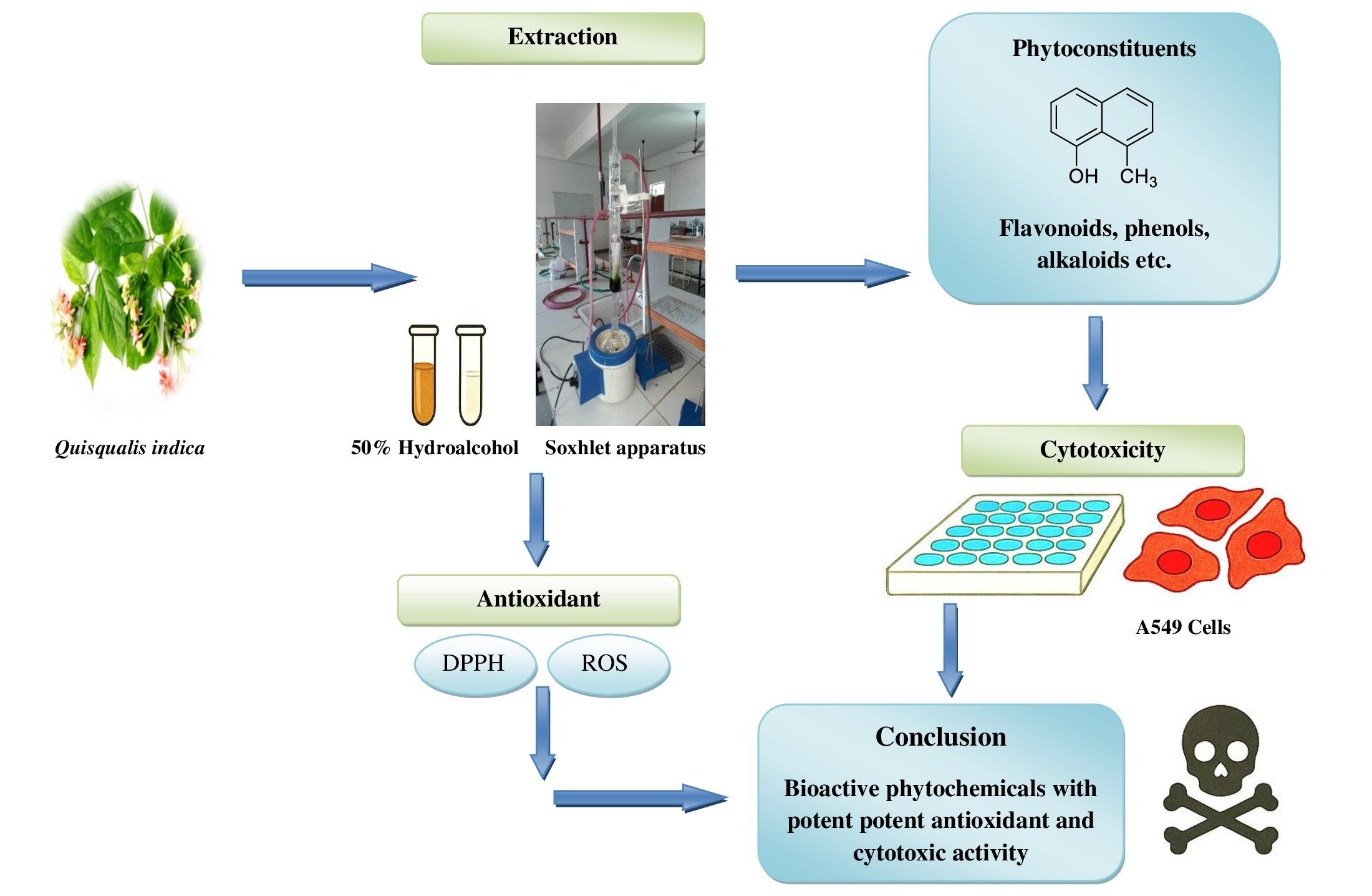
Background: The present study investigates the antioxidant and cytotoxic potential of the 50% hydroalcoholic extract of Quisqualis indica leaves. Methodology: Phytochemical screening was conducted to determine the presence of phenolics and flavonoids. TPC and TFC were analyzed using the Folin–Ciocalteu method and the aluminum chloride colorimetric assay, respectively. The antioxidant activity was evaluated through the DPPH radical scavenging assay at concentrations ranging from 10 to 100 µg/mL. Cytotoxicity was assessed in A549 human lung carcinoma cells using the MTT assay with extract concentrations from 0 to 1000 µg/mL. Results and Discussion: Phytochemical analysis confirmed the presence of phenolics and flavonoids, with total phenolic content measured as 9.25 ± 0.081 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE)/g 50% hydroalcoholic extract and total flavonoid content as 4.33 ± 0.24 mg quercetin equivalents (QE)/g 50% hydroalcoholic extract. Antioxidant activity was assessed using the DPPH radical scavenging assay across extract concentrations ranging from 10 to 100 μg/mL. The 50% hydroalcoholic extract exhibited a dose-dependent antioxidant effect with an IC50 value of 48.56 μg/mL. Cytotoxicity was evaluated against A549 human lung carcinoma cells using the MTT assay, with treatments administered at concentrations ranging from 0 to 1000 μg/mL. The extract demonstrated significant cytotoxicity with an IC50 value of 4.76 μg/mL. Conclusion: These findings suggest that Q. indica may serve as a potential source of bioactive compounds with antioxidant and anticancer activities, warranting further investigation through in vivo and mechanistic studies.
Downloads
References
Mahajan CP, Aher AN. A review on ethnobotanical, phytochemical and pharmacological activities of Quisqualis indica Linn. Res. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem., 9, 47 (2017) https://doi.org/10.5958/0975-4385.2017.00008.5.
Sahu K. Study of antioxidant and anti-diarrheal activity of whole plant of Madhumalti {Quisqualis indica Linn.}. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci., 29, 096–103 (2024) https://doi.org/10.30574/gscbps.2024.29.2.0417.
Nemade CT, Aher AN. Pharmacognostic Study and Establishment of Quality Parameters of Quisqualis indica Linn. Leaves. ECS Trans., 107, 14363–80 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1149/10701.14363ecst.
Kulshreshtha M, Chaudhary RK, Roy S, Shukla KS, Singh A, Singh MP. Pharmacological Investigation on Unraveling Mechanism of Action of Quisqualis indica Leaves for Predicted Treatment of Peptic Ulcer Disease. Curr. Funct. Foods, 1, (2023) https://doi.org/10.2174/2666862901666230320103455.
Chaudhary D, Srivastava R, Nagar H. Anti-allergic Assessment of Ethanol Extractives of Quisqualis Indica Linn. Curr. Bioact. Compd., 17, (2021) https://doi.org/10.2174/1573407216999201124222935.
Barik BS, Das S, Hussain T. Pharmacognostic Properties of Quisqualis indica Linn: Against Human Pathogenic Microorganisms: An Insight Review. European J. Med. Plants, 31, 87–103 (2020) https://doi.org/10.9734/ejmp/2020/v31i2030369.
Nemade CT, Aher AN. Quisqualis indica Linn.: HRLCMS/MS profiling and anti-asthma activity of leaf extracts. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci., 10, 13 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-024-00586-5.
Sahu J. Effects of Methanolic Extracts of Quisqualis Indica (aerial parts) on passive smoking induced Hyperlipidemia in Rats. J. Med. Pharm. Allied Sci., 1, 25–8 (2012) https://doi.org/10.55522/jmpas.V1I1.0005.
Rout PK, Kumar P, Rao YR, Kumar A, Bawankule DU, Singh R, Singh KB, Chanotiya CS, Naik SN. A quinoline alkaloid rich Quisqualis indica floral extract enhances the bioactivity. Nat. Prod. Res., 35, 1632–8 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2019.1634709.
Anjali P, Vivek J, Jigar P, Keyuri B, Vaibhavi S, Jayesh D, Mayank P, Devang P. Establishment of quality parameters of Quisqualis indica leaves through sophisticated analytical techniques. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop., 37, 289–98 (2022) https://doi.org/10.4314/bcse.v37i2.4.
Zhao Y, Zhang C, Liu W, Guo Z, Zhang Y, Wu Y, Wei C, Wu J, Yang X. Quinolines: A Promising Heterocyclic Scaffold for Cancer Therapeutics. Curr. Med. Chem., 32, 958–73 (2025) https://doi.org/10.2174/0109298673258512231013060222.
Çakmak O, Ökten S, Köprülü TK, Andac CA, Tekin Ş, Arslan SO. Highly Brominated Quinolines: Synthesis, Characterization, and Investigation of Anticancer Activities Supported by Molecular Dynamics. Chem. Biol. Drug Des., 105, (2025) https://doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.70120.
Pal P, Singh A. In-vitro Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activities of Quisqualis indica Linn. Leaves Extract. J. Adv. Biol. Biotechnol., 21, 1–13 (2019) https://doi.org/10.9734/jabb/2019/v21i130082.
Adwin Jose P, Dhaveethu Raja J, Sankarganesh M, Rajesh J. Evaluation of antioxidant, DNA targeting, antimicrobial and cytotoxic studies of imine capped copper and nickel nanoparticles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol., 178, 143–51 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.11.005.
Kulshreshtha M, Shukla KS, Tiwari GA, Singh MP, Singh A. Pharmacognostical, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Aspects of Quisqualis indica: An Update. J. Nat. Sci. Med., 1, (2018) https://doi.org/10.4103/JNSM.JNSM_20_18.
Sharma AK, Sati DM, Murti Y, Ved A, Yadav S, Singh A, Singh A, Singh MP, Nigam AK, Shukla KS, Kulshreshtha M. A comprehensive review on Chinese honeysuckle (Qusqualis indica): A Traditional Chinese plant. Toxicol. Reports, 13, 101768 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101768.
Kulshreshtha M, Srivastava G, Singh MP. Pharmacognostical, Anti-oxidant Activity and High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography Studies on Leaves of Quisqualis indica Linn. Curr. Tradit. Med., 4, 53–67 (2018) https://doi.org/10.2174/2215083804666180118095645.
Kim M-I, Yoon J-S, Oh M-H, Son R-H, Yeon S-H. Validation of Analytical Method of Quisqualic Acid for Standardization of Quisqualis indica Extract Powder (HU033). J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr., 50, 204–9 (2021) https://doi.org/10.3746/jkfn.2021.50.2.204.
Dai L, Yang L, Li Y, Li S, Yang D, Li Y, He D. Origin differentiation based on volatile constituents of genuine medicinal materials Quisqualis indica L. via HS‐GC‐MS, response surface methodology, and chemometrics. Phytochem. Anal., 35, 567–78 (2024) https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.3313.
Wu YS, Lee MF, Guad R Mac, Ozeer FZ, Velaga A, Subramaniyan V, Fuloria NK, Fuloria S, Choy KW, Lee SM, Gopinath SCB, Verma A, Lau TP. Insights on Anticancer Activities, Associated Phytochemicals and Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Quisqualis indica: A Mini Review. Sains Malaysiana, 52, 1749–58 (2023) https://doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2023-5206-11.
Baek JM, Kim HJ, Nam MW, Park HJ, Yeon SH, Oh MH, Yoon JS, Kwon HJ, Lee KP, Lim JH. Standardized Seed Extract of Quisqualis indica (HU-033) Attenuates Testosterone Propionate-Induced Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia via α1-Adrenergic Receptors and Androgen/Estrogen Signaling. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci., 24, 492–7 (2019) https://doi.org/10.3746/pnf.2019.24.4.492.
Kim D, Kwon H-J, Lim J-H, Kim J, Lee KP. Quisqualis indica extract ameliorates low urinary tract symptoms in testosterone propionate-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia rats. Lab. Anim. Res., 36, 26 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1186/s42826-020-00059-9.
Nortjie E, Basitere M, Moyo D, Nyamukamba P. Extraction Methods, Quantitative and Qualitative Phytochemical Screening of Medicinal Plants for Antimicrobial Textiles: A Review. Plants, 11, 2011 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11152011.
Habeeeb HM. A comparative phytochemical investigation and antioxidant activity of Quisqualis indica L. Diyala Agric. Sci. J., 16, 137–44 (2024) https://doi.org/10.52951/dasj.24160112.
Sari KRP, Ikawati Z, Danarti R, Hertiani T. Micro-titer plate assay for measurement of total phenolic and total flavonoid contents in medicinal plant extracts. Arab. J. Chem., 16, 105003 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.105003.
Do QD, Angkawijaya AE, Tran-Nguyen PL, Huynh LH, Soetaredjo FE, Ismadji S, Ju Y-H. Effect of extraction solvent on total phenol content, total flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity of Limnophila aromatica. J. Food Drug Anal., 22, 296–302 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2013.11.001.
Gulcin İ, Alwasel SH. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay. Processes, 11, 2248 (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11082248.
Akar Z, Küçük M, Doğan H. A new colorimetric DPPH • scavenging activity method with no need for a spectrophotometer applied on synthetic and natural antioxidants and medicinal herbs. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem., 32, 640–7 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2017.1284068.
Wang SY, Jiao H. Scavenging Capacity of Berry Crops on Superoxide Radicals, Hydrogen Peroxide, Hydroxyl Radicals, and Singlet Oxygen. J. Agric. Food Chem., 48, 5677–84 (2000) https://doi.org/10.1021/jf000766i.
Islam MN, Rauf A, Fahad FI, Emran T Bin, Mitra S, Olatunde A, Shariati MA, Rebezov M, Rengasamy KRR, Mubarak MS. Superoxide dismutase: an updated review on its health benefits and industrial applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr., 62, 7282–300 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.1913400.
Grela E, Kozłowska J, Grabowiecka A. Current methodology of MTT assay in bacteria – A review. Acta Histochem., 120, 303–11 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2018.03.007.
Kumar P, Nagarajan A, Uchil PD. Analysis of Cell Viability by the MTT Assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc., 2018, pdb.prot095505 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot095505.
Hayon T, Dvilansky A, Shpilberg O, Nathan I. Appraisal of the MTT-based Assay as a Useful Tool for Predicting Drug Chemosensitivity in Leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma, 44, 1957–62 (2003) https://doi.org/10.1080/1042819031000116607.
Hadavandsiri F, Allahqoli L, Rahimi Y, Salehiniya H, Ghazanfari Savadkoohi E, Akbari ME. Cancer incidence in Iran in 2016: A study based on the Iranian National Cancer Registry. Cancer Rep., 7, (2024) https://doi.org/10.1002/cnr2.1967.
Asadi M, Taghizadeh S, Kaviani E, Vakili O, Taheri‐Anganeh M, Tahamtan M, Savardashtaki A. Caspase‐3: Structure, function, and biotechnological aspects. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem., 69, 1633–45 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.2233.
Ahmed F, Aktar F, Rashid MA, Rahman MS. Free Radical Scavenging, Membrane Stabilizing and Thrombolytic Potentials of the Leaves of Quisqualis indica (L.). Bangladesh Pharm. J., 24, 99–104 (2021) https://doi.org/10.3329/bpj.v24i2.54707.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Ajay Verma, AKS Rawat

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
















